The History Of Halloween: A Scholarly Exploration
The History of Halloween: A Scholarly Exploration
Related Articles: The History of Halloween: A Scholarly Exploration
- Halloween 2024: A Journey Through Time And Tradition
- Happy Halloween Zeichnen 2024: A Spooktacular Guide To The Best Halloween Drawings
- Happy Halloween Text Art 2024: A Spooky Spectacular
- Halloween Movies: A Cinematic Journey From Horror To Camp
- Halloween: A Global Celebration With Ancient Roots
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The History of Halloween: A Scholarly Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The History of Halloween: A Scholarly Exploration
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Video about The History of Halloween: A Scholarly Exploration
- 4 The History of Halloween: A Scholarly Exploration
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Celtic Origins: The Festival of Samhain
- 4.3 Pagan Influences: Rituals and Beliefs
- 4.4 Christian Influences: All Saints’ Day and All Souls’ Day
- 4.5 The Name "Halloween"
- 4.6 Halloween Customs and Traditions
- 4.7 Cultural and Regional Variations
- 4.8 Conclusion
- 5 Closure
Video about The History of Halloween: A Scholarly Exploration
The History of Halloween: A Scholarly Exploration

Introduction
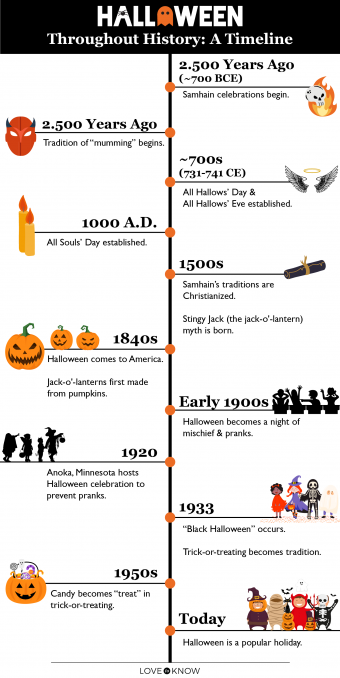
Halloween, a widely celebrated festival observed annually on October 31st, is steeped in a rich and multifaceted history that has evolved over centuries. Its origins can be traced back to ancient Celtic traditions, pagan rituals, and Christian influences, creating a complex tapestry of beliefs, customs, and symbolism. This article delves into the historical evolution of Halloween, examining its roots and the various cultural and religious influences that have shaped its present-day manifestations.
Celtic Origins: The Festival of Samhain
Halloween’s origins lie in the ancient Celtic festival of Samhain, celebrated by the Celts, who inhabited parts of Europe, including Ireland, Britain, and northern France. Samhain marked the end of the harvest season and the beginning of the Celtic new year, which occurred on November 1st.
According to Celtic beliefs, on the night of Samhain, the boundary between the worlds of the living and the dead blurred, allowing spirits and supernatural beings to cross over into the human realm. The Celts believed that on this night, the ghosts of the dead returned to their former homes, seeking food and warmth. To honor the spirits, the Celts would leave offerings of food and drink outside their homes and light bonfires to guide them.
Pagan Influences: Rituals and Beliefs
Over time, Samhain incorporated various pagan rituals and beliefs. One common practice was divination, as the Celts believed that on this night, the veil between the worlds was thin, making it easier to communicate with the spirits and predict the future. People would perform rituals such as bobbing for apples or carving turnips (later replaced by pumpkins) into lanterns, which were believed to ward off evil spirits.
Another significant pagan influence was the belief in the "Lord of the Dead," a supernatural figure who was said to rule over the realm of the dead. Offerings were made to this deity in the hope of appeasing him and preventing him from harming the living.
Christian Influences: All Saints’ Day and All Souls’ Day
In the 8th century, Pope Gregory IV established November 1st as a Christian holiday known as All Saints’ Day, intended to honor all Christian saints. This holiday was later followed by All Souls’ Day, observed on November 2nd, which commemorated the dead and prayed for their souls.
Over time, All Saints’ Day and All Souls’ Day became intertwined with Samhain, resulting in the blending of Christian and pagan traditions. The Christian influence brought about a shift in focus from honoring the dead to celebrating the saints and praying for the souls in purgatory.
The Name "Halloween"
The term "Halloween" is derived from the Scottish word "All Hallows’ Eve," which refers to the evening before All Saints’ Day. The name was first used in the 16th century and gradually became popularized throughout the English-speaking world.
Halloween Customs and Traditions
Throughout history, Halloween has been celebrated with a variety of customs and traditions. These include:
- Trick-or-Treating: This practice originated from the Celtic belief that spirits would visit homes on Samhain, seeking food and warmth. In return for offerings, the spirits would bless the household. Trick-or-treating evolved from this tradition, with children dressing up in costumes to represent the spirits and going door-to-door asking for treats.
- Costumes: Wearing costumes on Halloween is another tradition that has its roots in Celtic beliefs. The Celts believed that wearing animal skins or masks would protect them from evil spirits. Over time, costumes became more elaborate and varied, reflecting different characters, creatures, and themes.
- Jack-o’-Lanterns: Carving pumpkins or turnips into lanterns is a popular Halloween tradition that originated from the Celtic practice of using carved turnips to represent the Lord of the Dead. The lanterns were believed to guide lost spirits and ward off evil.
Cultural and Regional Variations
Halloween is celebrated in various ways across different cultures and regions. In the United States, Halloween is primarily a secular holiday focused on trick-or-treating, costume parties, and pumpkin carving. In Ireland, where the festival has its Celtic roots, Halloween is known as Oíche Shamhna and is still celebrated with bonfires, traditional games, and storytelling. In Mexico, Halloween is celebrated as Día de los Muertos (Day of the Dead), a two-day holiday that honors the deceased with elaborate altars, offerings, and festive celebrations.
Conclusion
Halloween is a festival with a rich and complex history, drawing upon ancient Celtic traditions, pagan rituals, and Christian influences. Its origins lie in the Celtic festival of Samhain, where the boundary between the worlds of the living and the dead was believed to blur. Over time, Halloween incorporated various pagan practices, such as divination, rituals, and beliefs in supernatural beings. The introduction of All Saints’ Day and All Souls’ Day by the Christian Church further influenced Halloween’s evolution, blending Christian and pagan elements.
Today, Halloween is celebrated worldwide with a variety of customs and traditions, including trick-or-treating, wearing costumes, carving pumpkins, and attending parties. While its manifestations may vary across cultures and regions, Halloween remains a vibrant and popular festival that continues to captivate people of all ages.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The History of Halloween: A Scholarly Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!